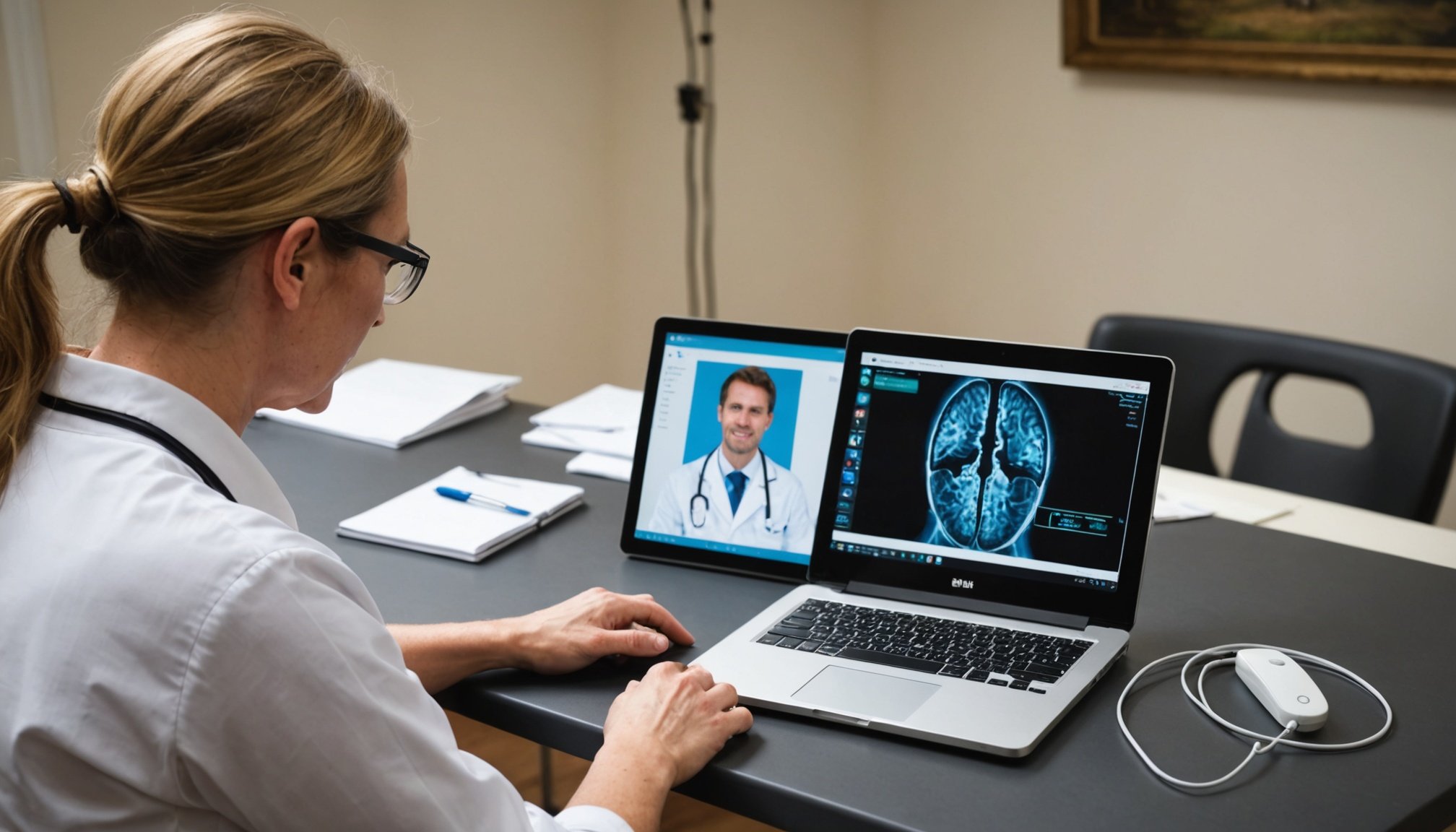
Overview of Telehealth in the UK
Telehealth in the UK is transforming how healthcare services are delivered. It refers to the use of digital communication technologies to access healthcare services remotely, making medical advice more accessible without the need for physical appointments. The scope of telehealth is broad, encompassing services such as virtual consultations, remote monitoring, and even digital therapy applications.
One of the significant benefits of telehealth is its ability to address healthcare disparities, particularly in rural healthcare settings. Rural communities often face challenges such as limited access to healthcare facilities and professionals. Telehealth bridges this gap by providing these populations with timely and crucial healthcare access, thus fostering healthcare innovation.
Have you seen this : Thriving in the virtual era: essential strategies for uk event planning firms to succeed in online conferences
The current state of telehealth in the UK reveals a growing acceptance and integration into healthcare systems. Over recent years, the trajectory of telehealth services has been upward, driven by technological advancements and increased demand for efficient healthcare delivery. Moreover, the COVID-19 pandemic acted as a catalyst, accelerating the adoption and implementation of telehealth services across the country. As the technology behind telehealth continues to evolve, so does its capacity to enhance care delivery.
Innovative Telehealth Strategies
In recent years, the UK has seen a surge in telehealth strategies aimed at revolutionising healthcare delivery. One of the most notable approaches is the integration of virtual consultations, which has significantly enhanced accessibility for patients. This method allows individuals, especially those in remote areas, to connect with specialists without the need for travel. It’s a boon for rural communities, reducing appointment times and travel costs while maintaining high-quality care.
This might interest you : Securing financial support: a comprehensive handbook for uk renewable energy startups to win government grants
A sterling example of service innovation is the deployment of mobile health units. These units navigate through rural regions, providing essential medical services where traditional healthcare delivery might not reach. They are equipped with the necessary tools for basic diagnostics and treatment, bridging the gap between urban and rural healthcare provision.
Furthermore, successful telehealth initiatives have been targeting these communities specifically to meet unique needs. For instance, some programs have tailored virtual consultations to focus on chronic disease management, fostering constant engagement between healthcare providers and patients.
Overall, these innovative telehealth strategies are not only reshaping how healthcare is delivered but also ensuring that all communities have equitable access to necessary medical services. These developments highlight the critical role of technology in expanding the reach and efficiency of healthcare systems.
Case Studies of Successful Telehealth Implementation
To illustrate the transformations in rural healthcare, we explore detailed case studies demonstrating effective telehealth strategies.
Case Study 1: Rural Health Connection Program
This successful telehealth program aimed to bridge healthcare gaps in isolated regions. Using advanced video conferencing and remote monitoring, it enabled specialists to provide consultations without patients needing to travel extensively. The implementation focused on deploying user-friendly platforms accessible even with limited internet connectivity, ensuring consistent healthcare delivery. Outcomes included reduced health disparities and increased patient satisfaction, as local communities reported improved access to specialist care and enhanced quality of life.
Case Study 2: Mobile Health Initiative in Appalachia
Addressing healthcare shortages, this initiative focused on integrating telehealth solutions via mobile clinics. Despite initial challenges such as resistance to technology and limited infrastructure, training sessions and community engagement ensured a successful rollout. Benefits included heightened disease prevention and management efforts, demonstrating tangible improvements in community health metrics like reduced hospital admissions and improved chronic disease management.
Case Study 3: Teletherapy Support System
Incorporating mental health support through digital platforms, this case highlighted the importance of accessible telehealth services. Providers noted positive feedback, with patients experiencing reduced stigma and enhanced therapy access. Noteworthy lessons included the necessity of continual technological updates and training to best support practitioners and patients, setting a precedent for future telehealth advancements.
Challenges and Barriers to Telehealth Adoption
Telehealth challenges are numerous, particularly in rural areas where healthcare accessibility is already limited. The primary issues revolve around integrating telehealth into rural healthcare barriers such as inadequate internet infrastructure, which makes reliable connectivity difficult to achieve. The lack of high-speed internet in many rural areas is a major impediment to seamless telehealth services, ultimately affecting patient outcomes and access.
Moreover, technology integration in these settings often encounters obstacles related to digital literacy. Many individuals, especially the elderly or those unfamiliar with recent technological advancements, may struggle with using telehealth platforms effectively, thus limiting the reach and efficiency of these services. A greater emphasis on education and training is essential to overcome this barrier, enabling patients and healthcare providers alike to benefit fully from telehealth’s potential.
Legislative and regulatory hurdles are another significant challenge. Frequently, policy-related challenges cause discrepancies in telehealth service provision, with variations in licensing and regulations across different jurisdictions. These issues necessitate a coordinated policy approach to standardize practices and ensure equitable access to telehealth, thus facilitating a smoother transition into digital healthcare solutions. Addressing these concerns is crucial for the widespread adoption and ultimate success of telehealth systems.
Best Practices for Telehealth Integration
To effectively integrate telehealth into healthcare systems, adopting a strategic approach is crucial. Healthcare providers should focus on several effective strategies to harness the full potential of telehealth services.
A critical first step is crafting a comprehensive telehealth integration plan. This plan should detail the scope of services, technology requirements, and logistical considerations. Additionally, providers must ensure that all stakeholders, including patients and staff, are engaged and informed about the telehealth initiatives.
Community engagement plays a vital role as well. Collaborating with local organisations and patient groups can foster trust and increase the adoption rate of telehealth services. By creating partnerships, healthcare providers can address specific community needs and ensure the services are both relevant and beneficial.
Training healthcare professionals is equally important. Implementing ongoing training and support mechanisms can help staff adapt to new technologies swiftly and confidently. This training should cover not only technological competence but also communication skills necessary for virtual consultations.
Finally, monitoring and evaluating the telehealth services is crucial to ensure continuous improvement. Gathering feedback from users and analysing usage data can provide insights into areas that require refinement, thus enhancing the effectiveness and reach of telehealth services.
The Future of Telehealth in the UK
The future of telehealth in the UK is poised for significant transformation as innovations in healthcare technology continue to evolve. These advancements are predicted to reshape telehealth services post-pandemic, leading to more effective and accessible healthcare systems.
Emerging technologies, such as artificial intelligence and machine learning, are expected to play a pivotal role. These technologies can provide personalised care and predictive analytics, revolutionising patient and practitioner interactions. The adaptability of these technologies allows for real-time monitoring, thereby promoting a proactive approach to healthcare.
Another crucial aspect of the future landscape includes strategic healthcare innovation aimed at reaching underserved rural areas. Current UK healthcare policy needs to foster infrastructural enhancements to bridge the digital divide. Increasing the availability of reliable internet access and telehealth education in rural communities is essential for widespread adoption.
Policy recommendations underscore the importance of a cohesive framework to support telehealth initiatives. By prioritising funding and research into infrastructure and training, the UK can ensure robust and efficient systems. These strategic moves would ensure telehealth is not a temporary solution but a permanent and integral part of healthcare delivery. Such measures, if implemented effectively, promise a healthcare revolution that benefits all citizens.